Collagen: what is it? Supplements, benefits
Health properties of Collagen
Fact Checked
×All the content published in our website is fact checked to validate its accuracy.
Visit our guidelines web page to learn more about our strict processes regarding how we review our content's sources: reliable and reputable journals, media websites, universities, colleges, organizations, and professionals.
Our articles are based on scientific evidence, and the references are included in its footnotes, which are clickable links to sound scientific papers.
First published: 11.Oct.2018
Overview: Collagen all you need to know
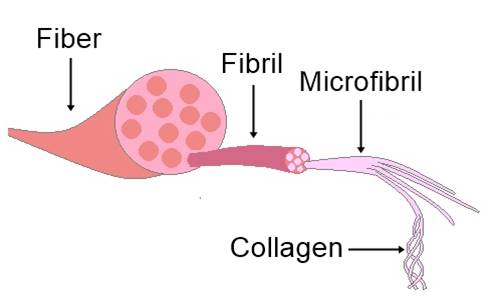
Collagen is a protein made by your body. It provides structure, cohesion and strenght to your bones, tendons, skin and organs.
The body's production of collagen declines with age and exposure to free radicals, leading to joint damage and aging skin. Supplementing with animal sourced collagen has been proven to support skin youthfullness, improve bone density and provide moderate joint health effects.
Learn about collagen, its types, origin, composition, its health benefits and why vegans and vegetarians should be aware of the negative effects of those dietws on collagen production.
References and Further Reading
(1) Linda Rath (2022). Can Collagen Supplements Help Arthritis?. Arthritis Foundation. Dec. 21, 2022, accessed Oct. 12, 2023
(2) Martínez-Puig D, Costa-Larrión E, Rubio-Rodríguez N, Gávez-Martin P. (2023). Collagen Supplementation for Joint Health: The Link between Composition and Scientific Knowledge. Nutrients. 2023 Mar 8;15(6):1332. doi: 10.3390/nu15061332. PMID: 36986062
(3) Zhu S, Huang M, Feng G, Miao Y, Wu H, Zeng M, Lo YM.(2018). Gelatin versus its two major degradation products, prolyl-hydroxyproline and glycine, as supportive therapy in experimental colitis in mice. Food Sci Nutr. 2018 Apr 16;6(4):1023-1031. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.639. PMID: 29983966
(4) de Miranda RB, Weimer P, Rossi RC. (2021). Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2021 Dec;60(12):1449-1461. doi: 10.1111/ijd.15518. Epub 2021 Mar 20. PMID: 3374270
(5) García-Coronado JM, et al. (2019). Effect of collagen supplementation on osteoarthritis symptoms: a meta-analysis of randomized placebo-controlled trials. Int Orthop. 2019 Mar;43(3):531-538. doi: 10.1007/s00264-018-4211-5. Epub 2018 Oct 27. PMID: 30368550
(6) König D, Oesser S, Scharla S, Zdzieblik D, Gollhofer A. (2018). Specific Collagen Peptides Improve Bone Mineral Density and Bone Markers in Postmenopausal Women-A Randomized Controlled Study. Nutrients. 2018 Jan 16;10(1):97. doi: 10.3390/nu10010097. PMID: 29337906
(7) León-López A et al., (2019). Hydrolyzed Collagen-Sources and Applications. Molecules. 2019 Nov 7;24(22):4031. doi: 10.3390/molecules24224031. PMID: 31703345
(8) Shaw G, Lee-Barthel A, Ross ML, Wang B, Baar K. (2016). Vitamin C-enriched gelatin supplementation before intermittent activity augments collagen synthesis. Am J Clin Nutr. 2017 Jan;105(1):136-143. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.116.138594. Epub 2016 Nov 16. PMID: 27852613
(9) Karlic H, Schuster D, Varga F, Klindert G, Lapin A, Haslberger A, Handschur M. (2008). Vegetarian diet affects genes of oxidative metabolism and collagen synthesis. Ann Nutr Metab. 2008;53(1):29-32. doi: 10.1159/000152871. Epub 2008 Sep 5. PMID: 18772587
About this Article
Collagen: what is it? Supplements, benefits, A. Whittall
©2023 Fit-and-Well.com, 13 Oct. 2023. Update scheduled for 13 Oct. 2025. https://www.fit-and-well.com/health/collagen-and-health.html
Tags: arthritis, gout, osteoarthritis, collagen, gelatin, rheumatoid arthritis, joints